Periodontal Disease
Home > Periodontal Disease
It is a common misconception that tooth loss comes with age. It is actually possible for teeth to last a lifetime. One of the best ways to achieve the goal of maintaining natural teeth is to avoid developing periodontal disease. Periodontal disease (literally translated as “around tooth” disease) is caused by the bacteria that targets the gum tissues around the teeth.
The symptoms of gum disease are not always apparent to people with the condition. Dental professionals recognize the signs of disease before they progress and are vital in the prevention and treatment process.
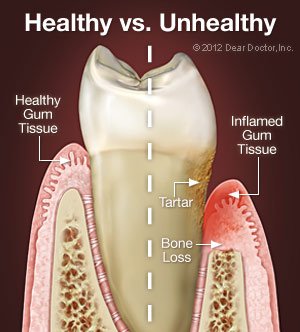
Virtually everyone who does not maintain good oral hygiene practices will go on to develop diseases of the teeth and gums, including gingivitis. Left untreated, gingivitis (mild gum disease) progresses to periodontitis (also called periodontal disease). Periodontitis results in bone loss around your teeth. Over time, gum tissues begin to detach from teeth and form pockets. Bacterial colonies thrive in these pockets and cannot be reached by brushing and flossing.
As periodontal disease advances and bone loss increases, teeth become loose and may fall out. While periodontal disease can have genetic components, it can be safely and successfully treated to prevent additional oral health issues and even heart disease and other health problems. Even at its most advanced stages, periodontal disease is a treatable condition.
Signs and Symptoms of Periodontal Disease
It is vital to understand that periodontal disease can be present without any obvious symptoms. This is especially true for smokers, who may experience decreased blood supply to the teeth and gums. With reduced blood supply, bleeding and swelling of the gums may not be as easy to detect.
Even in the absence of clear symptoms, there are some changes to oral health patients can keep an eye on. These include the following:
- Bleeding Gums – Some people think that bleeding gums indicate brushing too hard. Brushing hard can be bad for the gums, but should not cause bleeding. All bleeding in the gums should be considered a sign of impending or existing gum disease.
- Bad Breath – It is easy for plaque to gather in the pockets between teeth. Pockets provide an ideal living situation for bacterial colonies. Just as bacteria in the intestines are known to cause odors, bacteria in the mouth produces odorous compounds. These compounds lead to bad breath.
- Red and Swollen Gums – Gum inflammation is typically the very first indication that gum disease is present.
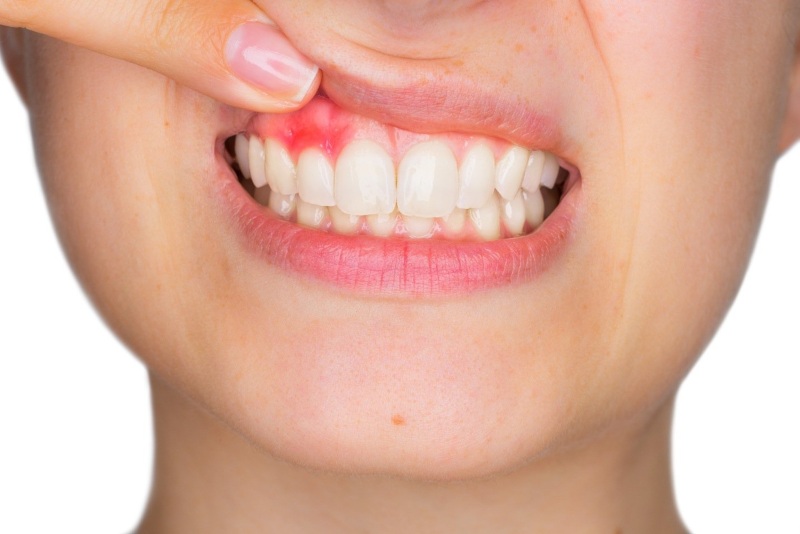
- Receding Gums – The phrase “long in the tooth” is used to describe the sight of receding gums. Gum tissue recedes away from enamel when gum disease is present and exposes the roots of teeth.
- Sensitivity in Teeth and Gums – When gums recede below the gum line, roots are exposed and become sensitive to both hot and cold stimuli.
- Periodontal Abscess – Bacteria can become so ingrained in a pocket that the area fills with pus. This enclosure eventually leads to a swollen and painful bump on the gums.
- Loose Teeth – Advanced periodontal disease leads to gum tissue and bone loss, which can cause teeth to become loose or migrate. Tooth loss is the standard result. This process is accelerated if you are biting down with excessive force or regularly clenching or grinding your teeth.
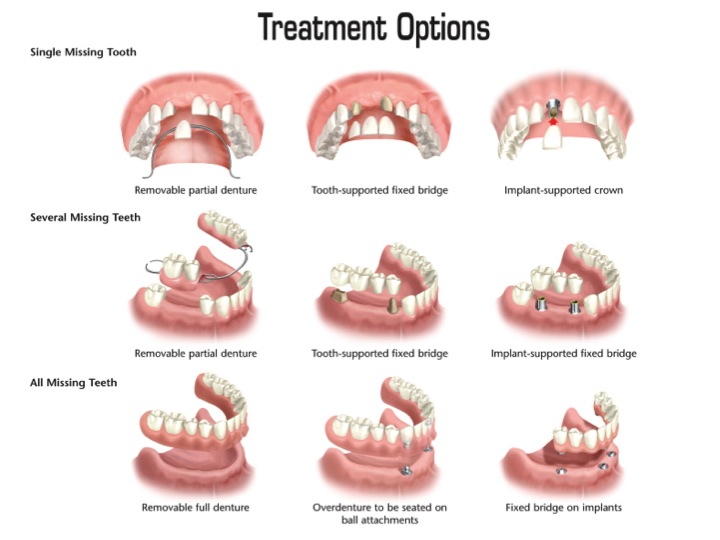
Treatment Options
All periodontal therapy will begin with an evaluation of existing oral hygiene techniques. If improvement is necessary, your dental team will demonstrate more effective techniques. From there, your team will remove plaque and all tartar present on root surfaces. This process is called scaling and root planing.
Root scaling and planing can be accomplished using hand instruments or ultrasonic instruments. Local antimicrobials and antibiotics may be used in more advanced cases to assist in healing from bacterial overgrowth and reduce the depth of gum pockets. If these efforts are successful, it is usually possible to avoid periodontal surgery.
If initial interventions are not successful in making significant changes, surgical procedures may be necessary. These procedures are used to remove the deep pockets between gum tissue and teeth. Different surgery techniques will be used to tackle different periodontal disease products. A combination of procedures may be used to reduce the number of required surgeries and decrease the overall cost of periodontal disease treatment.
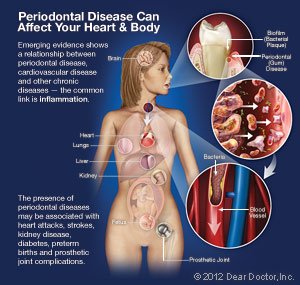
Periodontal Disease & Your Overall Health
Periodontal disease begins in your mouth but has been identified as one of the risk factors of cardiovascular disease (CVD), diabetes, and preterm birth. There are two possible reasons for the links between gum disease and chronic health conditions: increases in inflammation and bacterial proliferation. Inflammation and bacteria have both been identified as possible components involved in chronic health conditions.
Periodontal treatment is not merely an avenue toward improved oral health. It is also an important part of maintaining your overall health and limiting the weight of conditions stressing your immune system.
Preventive Strategies
The most effective strategy for warding off gum disease is employing consistent oral hygiene habits. The American Dental Association recommends brushing your teeth twice per day with a fluoride toothpaste and flossing at least once. Regular dental checkups and cleanings are necessary every 3-6 months because the instruments and techniques used in professional cleanings have access to areas that floss and toothbrushes cannot reach.
Early forms of gum disease can be seen during visual inspections of your teeth and gums. Pink gums that attach closely to the teeth are indicative of healthy gum tissue. The health of the bone supporting your teeth must be assessed by a dentist using dental x-rays.
Eating healthy, whole foods, reducing stress, and avoiding unhealthy habits like smoking can all contribute to improvements in your oral health and can help you retain your teeth permanently.
Our dental office in Elkin, NC has the tools and skills necessary to combat gum disease. Schedule an appointment with our team today!
Related Articles
Gums bleeding during brushing and flossing is often the first sign of gum disease. Learn what you can do to prevent gum disease and retain your teeth for your entire life.
Inflammation has been identified as a contributing factor in the development of cardiovascular disease, which can lead to heart attacks and strokes. The exact role inflammation plays remains unknown, but the connection is clear.
Millions of Americans will experience some amount of gum recession, or loss of the tissue that surrounds teeth. Receding gums have been tied to tooth sensitivity, tooth loss, and more. Periodontal plastic surgery has been used to combat gum recession.
Dentistry You Can Trust for the Whole Family
Testimonials